Thermal lensing and deformations from ring heaters
Ring heaters are used to introduce a thermal substrate lens
within an optic and also actuate on the surface curvature
of the mirror. Such devices allow us to compensate for
self-heating from laser beam absorption. The equations
implemented in finesse.thermal.ring_heater are from [33]
which analytically provides the substrate temperature profile
through a cylindrical optic when heated around its barrel
over a small area.
Steady state substrate temperature
import finesse
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import finesse.thermal.ring_heater as ring_heater
from finesse.materials import FusedSilica
finesse.init_plotting()
a = 0.17 # mirror radius
b = 56e-3 # LIGO ring heater position
c = 76e-3 # LIGO ring heater position
h = 0.2 # mirror thickness
w = 53e-3 # spot size radius
r = np.linspace(-a, a, 100) # radial points
z = np.linspace(-h/2, h/2, 100) # longitudinal points
material = FusedSilica
T_rh_per_W = ring_heater.substrate_temperature(r, z, a, b, c, h, material)
plt.pcolormesh(r, z, T_rh_per_W, rasterized=True, shading='auto')
plt.colorbar(label='T-$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{ext}}$ [K/W]')
plt.xlabel("Radius [m]")
plt.ylabel("Depth [m]")
Text(0, 0.5, 'Depth [m]')
The total substrate thermal lens optical path difference can also be
computed using the finesse.thermal.ring_heater.thermal_lens() method, again
returning a distortion per Watt of power ring heater power absorbed
by the mirror.
Z_rh_per_W = ring_heater.thermal_lens(r, a, b, c, h, material)
plt.plot(r, Z_rh_per_W)
plt.xlabel("Radius [m]")
plt.ylabel("OPD [m/W]")
Text(0, 0.5, 'OPD [m/W]')
Steady state Thermoelastic deformation
The note [34] describes how to calculate the thermal deformation of
surfaces due to an arbitrary ring heater profile around the barrel of a mirror.
surface_deformation(),
substrate_deformation_depth() implement this
calculation. In the examples below we plot the results for an Advanced LIGO
like test mass and ring heater setup.
import finesse
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import finesse.thermal.ring_heater as ring_heater
from finesse.materials import FusedSilica
finesse.init_plotting(fmts=["png"])
a = 0.17
b = 50e-3
c = 70e-3
h = 0.2
z = np.linspace(-h / 2, h / 2, 100)
material = FusedSilica
a = 170e-3 # radius of optic [m]
h = 0.2 # thickness of optic [m]
r = np.linspace(-a, a, 20) # radial points along optic
z = np.array([-h / 2, +h / 2]) # depth points along optic
dz = ring_heater.substrate_deformation_depth(r, z, a, b, c, h, material)
AR = dz[0, :] - dz[0, :].min()
HR = dz[1, :] - dz[1, :].max()
plt.plot(r, AR / 1e-9, label="z = -h/2")
plt.plot(r, HR / 1e-9, label="z = +h/2")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("r [m]")
plt.ylabel("Relative surface change [nm]")
plt.title("HR and AR surface deformation from a ring heater")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'HR and AR surface deformation from a ring heater')
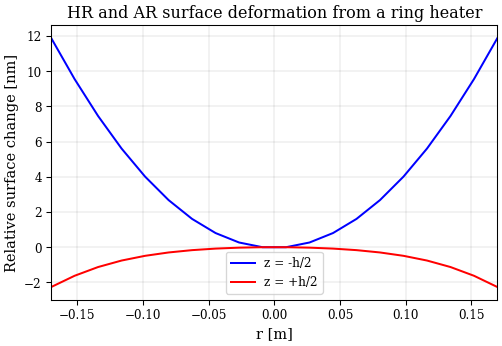
Or just the HR surface change:
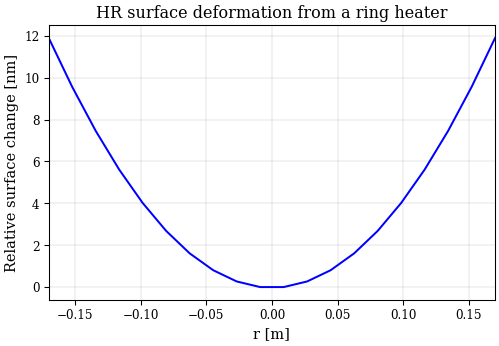
dz = ring_heater.surface_deformation(r, a, b, c, h, material)
plt.plot(r, dz / 1e-9, label="z = 0")
plt.xlabel("r [m]")
plt.ylabel("Relative surface change [nm]")
plt.title("HR surface deformation from a ring heater")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'HR surface deformation from a ring heater')